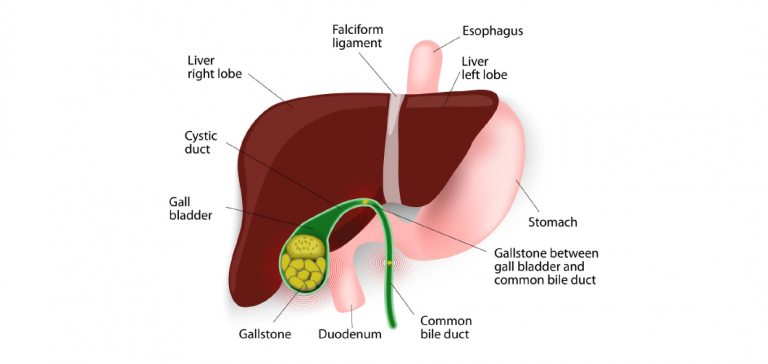
Gallstones are formed when bile, which is normally fluid, solidifies and hardens into small deposits in the gall bladder. The gallbladder is a part of the digestive system and is responsible for storing and releasing bile, which the liver produces, into the small intestine. Bile is essential for digestion since it helps in breaking down fat contents in the food.
Understanding gall stones
Gallstones are quite common in both men and women. Although the number and size of the stones can vary person to person, gallstones typically range in the size from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter.
Doctors usually advise a wait-and-watch policy for gallbladder stones when there is no report of pain. However, when the patient starts experiencing symptoms, doctors explore other treatment options including surgery.
Gallstones produce a variety of symptoms such as nausea, bloating, vomiting and abdominal pain. The most common symptom experienced is the however, abdominal pain.
Why should gall bladder be removed (and not only gallstone removal)?
Removal of the gallbladder is often recommended as a treatment option for gall bladder patients for a number of reasons, especially since it is a non-essential organ. Doctors mandatorily advise the removal of gallbladder when it is inflamed and infected, as the infection can turn life-threatening. In other cases, doctors advise removing the gall bladder when the pain and discomfort become very severe during an attack. It is also advised when the patient suffers repeatedly from gallstone attacks.
The removal of the gallbladder is usually advised for the following reasons:
Gall Stone Removal Process: Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Today laparoscopy is the most preferred form of surgery for removing the gallbladder. It is a far less invasive procedure than the traditional open cholecystectomy which requires a large incision in the abdomen.
As a part of the laparoscopic surgery, a small incision, less than an inch, is made in the navel and the surgeon inserts thin tubes that have a light, a camera and special surgical instruments using which the procedure is carried out. The patient recovers faster as a result of experiencing lesser trauma, lesser pain and lesser blood loss. It also results in lesser complications thus making it safer than open surgery.